What is Simple Harmonic Motion?
Simple Harmonic Motion is a special type of periodic motion, where the restoring force (F) is directly proportional to the displacement (x) and acts in the opposite direction of displacement. For example, the periodic motion of a pendulum and vibration of a stretched string are famous examples of simple harmonic motion.
So we can write that, F ∝ -x [ As the displacement is in the opposite direction of restoring force]
Or, F = – kx, here ‘k’ is the force constant.
Mathematical representation of Simple Harmonic Motion
Suppose a body is vibrating with a restoring force F at a particular time. At that moment, the displacement of the body from its equilibrium position is x. So we can write that, F ∝ -x [ As the displacement is in the opposite direction of restoring force]
Or, F =- kx, here ‘k’ is the force constant.
Angular frequency (ω) of Simple Harmonic Motion –
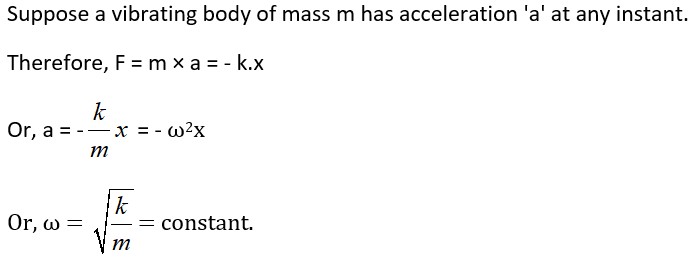
Another Way, a simple harmonic motion can also be expressed as, y = a sinωt
Or, y = a cosωt, where ω is the angular frequency of the vibrating body.
Hence, if the force on a particle varies as F ∝ – x, then the particle’s position varies as x = A sin(ωt + ϕ), where x is the displacement of the particle with respect to the equilibrium position.
Frequently Asked Questions about Simple Harmonic Motion – FAQs
We know that restoring force, F ∝ – x, And, The displacement of the particle, x = A sin (ωt + ϕ). Now, since the maximum and minimum values of the sine function can be +1 and –1, respectively, Thus the maximum displacement (x) of the particle is bounded between (–A) and (A).
The name SHM comes from the sine function; sine is a periodic and bounded function referred to as harmonic function, known as simple harmonic function. Force (F ∝ – x) is the reason for SHM, where periodicity and oscillatory motion are associated.
The rate of change of phase (?) in the Simple Harmonic Motion of a particle is known as the Angular frequency of the vibrating body.
Mean position: The magnitudes of force (F) and acceleration (a) are zero at the mean position. The velocity (v) possesses its maximum value, |vmax| = Aω, at the mean position.
Extreme position: At two extreme positions – The magnitude of velocity is zero, and the acceleration possesses its maximum value at the extreme position.
Simple Harmonic Motion is a special type of periodic motion, where the restoring force (F) is directly proportional to the displacement (x) and acts in the opposite direction of displacement. For example, the periodic motion of a pendulum and vibration of a stretched string are famous examples of simple harmonic motion.